
Figure legend: confocal image of a 20 micron tick cryosection of a murine acellular skeletal muscle matrix (laminin staining, red)
Through this blog I present and share my scientific interests and professional skills
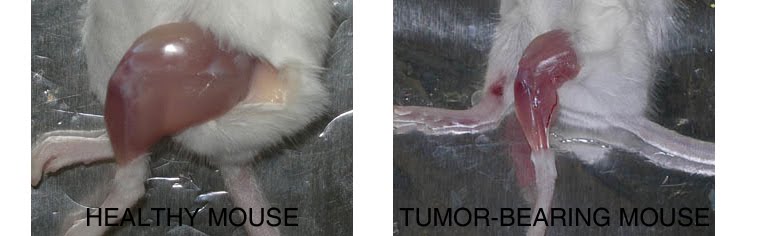
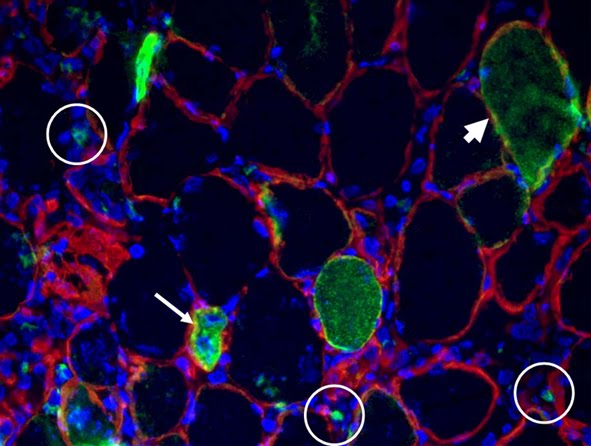
Background and rationale.
Tissue engineering lies at the interface of regenerative medicine and developmental biology, and represent an innovative and multidisciplinary approach to build organs and tissues (Ingber and Levin, Development 2007). The skeletal muscle is a contractile tissue characterized by highly oriented bundles of giant syncytial cells (myofibers) and by mechanical resistance. Contractile, tissue-engineered skeletal muscle would be of significant benefit to patients with muscle deficits secondary to congenital anomalies, trauma, or surgery. Obvious limitations to this approach are the complexity of the musculature, composed of multiple tissues intimately intermingled and functionally interconnected, and the big dimensions of the majority of the muscles, which imply the involvement of an enormous amount of cells and rises problems of cell growth and survival (nutrition and oxygen delivery etc.). Two major approaches are followed to address these issues. Self-assembled skeletal muscle constructs are produced in vitro by delaminating sheets of cocultured myoblasts and fibroblasts, which results in contractile cylindrical “myooids.” Matrix-based approaches include placing cells into compacted lattices, seeding cells onto degradable polyglycolic acid sponges, seeding cells onto acellularized whole muscles, seeding cells into hydrogels, and seeding nonbiodegradable fiber sheets. Recently, decellularized matrix from cadaveric organs has been proven to be a good scaffold for cell repopulation to generate functional hearts in mice (Ott et al. Nature Medicine 2008).
I have obtained cultures of skeletal muscle cells on conductive surfaces, which is required to develop electronic device–muscle junctions for tissue engineering and medical applications1. I aim to exploit this system for either recording or stimulation of muscle cell biological activities, by exploiting the field effect transistor and capacitor potential of the conductive substratum-cell interface. Also, we are able to create patterned dispositions of molecules and cells on gold, which is important to mimic the highly oriented pattern myofibers show in vivo.
I have found that Static magnetic fields enhance skeletal muscle differentiation in vitro by improving myoblast alignment2. Static magnetic field (SMF) interacts with mammal skeletal muscle; however, SMF effects on skeletal muscle cells are poorly investigated. 80 +/- mT SMF generated by a custom-made magnet promotes myogenic cell differentiation and hypertrophy in vitro. Finally, we have transplanted acellular scaffolds to study the in vivo response to this biomaterial3, which we want to exploit for tissue culture and regenerative medicine of skeletal muscle.
The specific aims of my current research are:
1) to increase and optimize the production and alignment of myogenic cells and myotubes in vitro;
2) to manipulate the niche of muscle stem cells aimed at ameliorating their regenerative capacity in vivo;
3) to develop muscle-electrical devices interactions. We plan to exploit the cell culture system on conductive substrates for either recording or stimulation of muscle cell biological activities, by exploiting the field effect transistor and capacitor potential of the conductive substratum-cell interface.
REFERENCES
1) Coletti D. et al., J Biomed Mat Res 2009; 91(2):370-377.
2) Coletti D. et al., Cytometry A. 2007;71(10):846-56.
3) Perniconi B. et al. Biomaterials, 2011 in press


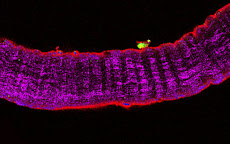
Research Unit: Regulatory Mechanisms of Normal and Pathologic Differentiation
Laboratory 21: Skeletal Muscle Homeostasis
@
Department of Anatomical, Histological, Forensic Sciences and Ortopedics - Section of Histology and Medical Embryology
Via Scarpa, 16
00161 Rome Italy
tel +39 0649766577; fax +39 064462854;
email: dario.coletti@uniroma1.it
skipe dario.coletti
profile web page (click English in the menu for English version): http://dariocoletti.site.uniroma1.it/
===================================
Research Unit: Biological Adaptation and Ageing B2A
Laboratory of Genetics and Patho-physiology of Muscle Tissues - GPPTM
@
University Pierre et Marie Curie Paris 6
Institute of Biology Paris-Seine
Research Unit B2A CNRS UMR 8256 - INSERM ERL U1164 - UPMC P6
7, quai Saint Bernard - case 256
Bat A, 6me étage
75252 Paris Cedex 5 France
telephone: +33 (0) 1 44 27 34 75, -2200 fax: +33 (0) 1 44 27 21 35
courriel: dario.coletti@upmc.fr

Adamo S, Pigna E, Lugarà R, Moresi V, Coletti D, Bouché M. Skeletal muscle: a significant novel neurohypophyseal hormon-secreting organ. Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 8;9:1885. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01885. eCollection 2018. No abstract available. PMID: 30670984
Giuriati W, Ravara B, Porzionato A, Albertin G, Stecco C, Macchi V, Caro R, Martinello T, Gomiero C, Patruno M, Coletti D, Zampieri S, Nori A. Muscle spindles of the rat sternomastoir muscle. Eur J Transl Myol. 2018 Dec 13;28(4):7904. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2018.7904. eCollection 2018 Nov 2. PMID: 30662700
Garcia M, Seelaender M, Sotiropoulos A, Coletti D, Lancha AH Jr. Vitamin D, muscle recovery, sarcopenia, cachexia, and muscle atrophy. Nutrition. 2019 Apr;60:66-69. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.09.031. Epub 2018 Oct 7. Review. PMID: 30529188
Ballini A, Cantore S, Scacco S, Coletti D, Tatullo M. Mesenchymal stem cells as promoters, enhancers, and playmakers of the translational regenerative medicine 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018 Oct 30;2018:6927401. doi: 10.1155/2018/6927401. eCollection 2018. No abstract available. PMID: 30510586
Pigna E, Sanna K, Coletti D, Li Z, Parlakian A, Adamo S, Moresi V. Increasing autophagy does not affect neurogenic muscle atrophy. Eur J Transl Myol. 2018 Aug 23;28(3):7687. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2018.7687. eCollection 2018 Jul 10. PMID: 30344980
Ravara B, Gobbo V, Incendi D, Porzionato A, Macchi V, De Caro R, Coletti D, Martinello T, Patruno M. Revisiting the peculiar regional distribution of muscle fiber types in rat Sternomastoid Muscle. Eur J Transl Myol 2018; 28 (1): 117-123. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2018.7302
Langlois B, Belozertseva E, Parlakian A, Bourhim M, Gao-Li J, Blanc J, Tian L, Coletti D, Labat C, Ramdame-Cherif Z, Challande P, regnault V, Lacolley P, Li Z. Vimentin knockout results in increased expression of sub-endothelial basement membrane components and carotid stiffness in mice. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):11628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12024-z
Baccam A, Hassani M, Sviercovish-Benoni A, Adamo S, Moresi V, Coletti D. Basking in their Niche: Stem Cells with Myogenic Potential as a Target to Combat Cachexia. Curr Updates in Stem Cell Res and Ther. 2017; 1: 1.1
Ballini A, Scacco S, Coletti D, Pluchino S, Tatullo M. Mesenchymal stem cells as promoters, enhancers, and playmakers of the translational regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Int Volume 2017, Article ID 3292810, 2 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3292810
Coletti D, Adamo S, Moresi V. Of faeces and sweat. How much a mouse is willing to run: having a hard time measuring spontaneous physical activity in different mouse sub-strains. Eur J Transl Myol 2017; 27(1):67-70. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2017.6483
Carotenuto F, Coletti D, Di Nardo P, Teodori L. α-Linolenic Acid Reduces TNF-Induced Apoptosis in C2C12 Myoblasts by Regulating Expression of Apoptotic Proteins. Eur J Transl Myol. 2016 Nov 17;26(4):6033. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2016.6033.
Mazzotti AL, Coletti D. The Need for a Consensus on the Locution "Central Nuclei" in Striated Muscle Myopathies. Front Physiol. 2016; 7:577.
Coletti D, Daou N, Hassani M, Li Z, Parlakian A. Serum Response Factor in Muscle Tissues: From Development to Ageing. Eur J Trans Myol. 2016 Jun 22;26(2):6008. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2016.6008.
Pigna E, Berardi E, Aulino P, Rizzuto E, Zampieri S, Carraro U, Kern H, Merigliano S, Gruppo M, Mericskay M, Li Z, Rocchi M, Barone R, Macaluso F, Di Felice V, Adamo S, Coletti D, Moresi V. Aerobic Exercise and Pharmacological Treatments Counteract Cachexia by Modulating Autophagy in Colon Cancer. Sci Rep. 2016 May 31;6:26991. doi: 10.1038/srep26991 + supplemetal data
Carotenuto F, Albertini MC, Coletti D, Vilmercati A, Campanella L, Darzynkiewicz Z, Teodori L. How Diet Intervention via Modulation of DNA Damage Response through MicroRNAs May Have an Effect on Cancer Prevention and Aging, an in Silico Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 19;17(5). pii: E752. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050752
Carotenuto F, Costa A, Albertini MC, Rocchi MB, Rudov A, Coletti D, Minieri M, Di Nardo P, Teodori L. Dietary Flaxseed Mitigates Impaired Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: in Vivo, in Vitro and in Silico Studies. Int J Med Sci. 2016 Feb 18;13(3):206-19. doi: 10.7150/ijms.13268.
Coletti D, Aulino P, Pigna E, Barteri F, Moresi V, Annibali D, Adamo S, Berardi E. Spontaneous Physical Activity Downregulates Pax7 in Cancer Cachexia. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:6729268. doi: 10.1155/2016/6729268
Carraro U, Coletti D, Kern H. The Ejtm Specials "The Long-Term Denervated Muscle". Eur J Transl Myol. 2014 Mar 27;24(1):3292. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2014.3292. No abstract available.
Barone R, Macaluso F, Sangiorgi C, Campanella C, Marino Gammazza A, Moresi V, Coletti D, Conway de Macario E, Macario AJ, Cappello F, Adamo S, Farina F, Zummo G, Di Felice V. Skeletal muscle Heat shock protein 60 increases after endurance training and induces peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 α1 expression. Sci Rep. 2016; v6:19781. doi: 10.1038/srep19781
Coletti D, Adamo S. Will exercise mimetics hold promise? J Pharmacovigilance 3: e138, 2015. doi:10.4172/2329-6887.1000e138
Aulino P, Costa A, Chiaravalloti E, Perniconi B, Adamo S, Coletti D, Marrelli M, Tatullo M, Teodori L. Muscle extracellular matrix scaffold is a multipotent environment. Int J Med Sci 12(4):336-40, 2015. doi: 10.7150/ijms.10761. ECollection 2015.
Di Felice V, Forte G, Coletti D. Biomaterials and bioactive molecules to drive differentiation in striated muscle tissue engineering. Front Physiol. 6:52, 2015. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00052. eCollection 2015
Moresi V, Marroncelli N, Coletti D, Adamo S. Regulation of skeletal muscle development and homeostasis by gene imprinting, histone acetylation and microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. pii: S1874-9399(15)00039-5, 2015. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.01.002. [Epub ahead of print]
Perniconi B*, Coletti D*, Aulino P, Costa A, Aprile P, Santacroce L, Chiaravalloti E, Coquelin L, Chevallier N,Teodori L, Adamo S, Marrelli M,Tatullo M. Muscle acellular scaffold as a biomaterial: effects on C2C12 cell differentiation and interaction with the murine host environment Front Physiol, 2. 5:354, 2014. * = equal contribution
Li Z, Parlakian A, Coletti D, Alonso-Martinez S, Hourdé C, Joanne P, Gao-Li J, Blanc J, Ferry A, Paulin D, Xue Z, Agbulut O. Synemin acts as a regulator of signalling molecules in skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Cell Sci. 3. 112(7):1035-4, 2014. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301076
Bouché M, Muñoz-Cánoves P, Rossi F, Coletti D. Inflammation in muscle repair, aging and myopathies. Biomed Res Int. 2014:821950, 2014. doi: 10.1155/2014/821950
Perniconi B, Coletti D. Skeletal muscle tissue engineering: best bet or black beast? Front Physiol, 5:255, 2014. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00255. eCollection 2014.
Teodori L, Costa A, Marzio R, Perniconi B, Coletti D, Adamo S, Gupta B, Tarnok A. Native extracellular matrix: a new scaffolding platform for repair of damaged muscle. Front Physiol, 5:218, 2014. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00218. eCollection 2014.
Costa A, Rossi E, Scicchitano BM, Coletti D, Moresi V, Adamo S. Neurohypophyseal hormones: novel actors of striated muscle development and homeostasis. Eur J Trans Myol - Basic Appl Myol 2014; 24 (3): 217-225
Teodori L, Giovannetti A, Albertini MC, Rocchi M, Perniconi B, Valente MG, Coletti D. Static magnetic field modulates X-ray-induced DNA damage in human glioblastoma primary cells. J Rad Res, 2014 Mar 1;55(2):218-27. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrt107
He WA, Berardi E, Cardillo VM, Acharyya S, Aulino P, Thomas-Ahner J, Wang J, Bloomston M, Muscarella P, Nau P, Shah N, Butchbach ME, Ladner K, Adamo S, Rudnicki MA, Keller C, Coletti D, Montanaro F, Guttridge DC. NF-κB-mediated Pax7 dysregulation in the muscle microenvironment promotes cancer cachexia. J Clin Invest. 2013 Nov 1;123(11):4821-35.
+ J Clin Invest Supplemental material
Coletti D, Teodori L, Li Z, Beranudin JF, Adamo S. Restoration versus reconstruction: cellular mechanisms of skin, nerve and muscle regeneration compared. BMC Regen Med Res, 2013, 1:4 available at: http://www.regenmedres.com/content/1/1/4
Galmiche G, Labat C, Mericskay M, Ait Aissa K, Blanc J, Retailleau K, Bourhim M, Coletti D, Loufrani L, Gao-Li J, Feil R, Challande P, Henrion D, Decaux JF, Regnault V, Lacolley P, Li Z. Inactivation of Serum Response Factor Contributes To Decrease Vascular Muscular Tone and Arterial Stiffness in Mice. Circ Res. 2013 Mar 29;112(7):1035-45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301076.
Coletti D, Berardi E, Aulino P, Rossi E, Moresi V, Li Z, Adamo S. Substrains of inbred mice differ in their physical activity as a behavior. The ScientificWorld Journal, Article ID 237260, 2013.
Perniconi B, Costa A, Aulino P, Teodori L, Adamo S, Coletti D. The pro-myogenic environment provided by whole organ scale acellular scaffolds from skeletal muscle. Biomaterials, 32(31):7870-82, 2011.
Toschi A., Severi A., Coletti D., Catizone A., Musarò A., Molinaro M., Nervi C., Adamo S., Scicchitano B.M.Skeletal muscle regeneration in mice is stimulated by local overexpression of V1a-vasopressin receptor. Mol Endocrinol, 25(9):1661-73, 2011.
Aulino P., Berardi E., Cardillo V.M., Rizzuto E., Perniconi B., Ramina C., Padula F., Spugnini E.P., Baldi A., Faiola F., Adamo S., Coletti D. Molecular, cellular and physiological characterization of the cancer cachexia-inducing C26 colon carcinoma in mouse. BMC Cancer,10(1):363, 2010*. * ranked 'Highly accessed'
Moresi V., Garcia-Alvarez G., Pristerà A., Rizzuto E., Albertini M.C., Rocchi M., Marazzi G., Sassoon D., Adamo S., Coletti D. Modulation of caspase activity regulates skeletal muscle regeneration and function in response to vasopressin and tumor necrosis factor. PLoSONE, 4(5):e5570, 2009.
Coletti D., Scaramuzzo F.A., Montemiglio L.C., Pristerà A., Teodori L., Adamo S., Barteri M. Culture of skeletal muscle cells in unprecedented proximity to a gold surface. J Biomed Mat Res: Part A, 91(2):370-377, 2009.
Coletti D., Adamo S. Highlights on Cachexia, from the 4th Cachexia Conference Tampa (FL), 6-9 Dec 2007. Basic Appl Myol, 18(5): 109-114, 2008.
Perniconi B., Albertini M.C., Teodori L., Belli L., Rocchi M., Coletti D. A meta-analysis on a therapeutic dilemma: to exercise or not to exercise in cachexia. Basic Appl Myol, 18(5): 105-120, 2008.
Schwarzkopf M., Coletti D., Marazzi G., Sassoon D. Chronic p53 activity leads to skeletal muscle atrophy and muscle stem cell perturbation. Basic Appl Myol, 18(5): 131-138, 2008.
Berardi E., Aulino P., Murfuni I., Toschi A., Padula F., Scicchitano B.M., Coletti D.*, Adamo S. Skeletal muscle is enriched in hematopoietic stem cells and not inflammatory cells in cachectic mice. Neurol Res, 30(2):160-169, 2008. * = corresponding autho
Moresi V., Pristerà A. , Scicchitano B.M., Molinaro M., Teodori l., Sassoon D., Adamo S., Coletti D. TNF inhibition of skeletal muscle regeneration is mediated by a caspase dependent stem cell response. Stem Cells, 26(4):997-1008, 2008.
Coletti D., Teodori L., Albertini M.C., Rocchi M., Pristerà A., Fini M., Molinaro M. Adamo S. Static magnetic fields enhance skeletal muscle differentiation in vitro by improving myoblast alignment. Cytometry: Part A, 71(10):846-56, 2007.
Musarò A., Giacinti C., Pelosi L., Dobrowolny G., Barberi L., Nardis C., Coletti D., Scicchitano B.M., Adamo S., Molinaro M. Stem Cell-mediated muscle regeneration and repair in aging and neuromuscular diseases. Eur J Histochem, 51(1):35-44, 2007.
Moresi V., Adamo S., Coletti D. Bimodal effects of TNF-alpha on differentiation and hypertrophy of skeletal muscle cell cultures. Basic Appl Myol, 16(5&6): 163-168, 2006.
Coletti D., Belli L., Adamo S. Cachexia: novel perspectives for an old syndrome. Basic Appl Myol, 16(5&6): 131-139, 2006.
Coletti D. *, Schwarzkopf M.*, Marazzi G., Sassoon D. Muscle cachexia depends upon a p53-PW1/Peg3 dependent pathway. Genes and Dev, 20(24):3440-52, 2006. * = equal contribution
Coletti D., Moresi V., Molinaro M., Adamo S., Sassoon D. Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha gene transfer induces cachexia and inhibits muscle regeneration. Genesis, 43(3):119-27, 2005.
Cannavo' A., Ceci P., Cortesi M., Coletti D., Adamo S., Naro F., Tomei F. I PCB causano necrosi dei mioblasti L6C5. G Ital Med Lav Ergon, 27(2):244-9, 2005.
De Arcangelis V., Coletti D., Canato M., Molinaro M., Adamo S., Reggiani C., Naro F. Hypertrophy and transcriptional regulation induced in myogenic cell line L6-C5 by an increase of extracellular calcium. J Cell physiol, 202(3):787-95, 2005.
Cannavò A., Ceci P., Coletti D., Cortesi M., Papa M., Vivarelli E., Tomei F., Adamo S., Fabio N. Toxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls in myogenic cells. J Health Sci, 50(1):33-41, 2004.
De Arcangelis V., Coletti D., Conti M., Lagarde M., Molinaro M., Adamo S., Nemoz G., Naro F. IGF-I-induced differentiation of L6 myogenic cells requires the activity of cAMP-phosphodiesterase. Mol Biol Cell,14(4):1392-404, 2003.
Naro F., De Arcangelis V., Coletti D., Molinaro M., Zani B., Vassanelli S., Reggiani C., Teti A., Adamo S. Increase in cytolosolic Ca2+ induced by elevation of extracellular Ca2+ in skeletal myogenic cells. Am J Cell Physiol - Cel Physiol, 284(4):C969-76, 2003.
Teodori L., Gohde W., Valente M.G., Tagliaferri F., Coletti D., Perniconi B., Bergamaschi A., Cerella C., Ghibelli L. Static magnetic fields affect calcium fluxes and inhibit stress-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Cytometry, 49(4):143-9, 2002.
Coletti D., Yang E., Marazzi G., Sassoon D. TNF-alpha inhibits skeletal myogenesis through a PW1-dependent pathway by recruitment of caspase pathways. EMBO J, 21(4):631-642, 2002.
Coletti D., Palleschi S., Silvestroni L., Cannavo' A., Vivarelli E., Tomei F., Molinaro M., Adamo S. Polychlorobiphenyls inhibit skeletal muscle differentiation in culture. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 175(3):226-233, 2001
Verde I., Pahlke G., Salanova M., Zhang G., Wang S., Coletti D., Onuffer J., Jin SL., Conti M. Myomegalin is a novel protein of the golgi/centrosome that interacts with a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem, 276(14):11189-98, 2001.
Coletti D., Palleschi S., Silvestroni L., Tomei F., Molinaro M., Adamo S. Surface remodeling associated with vasopressin-induced membrane traffic in L6 myogenic cells. Arch Histol Cytol, 63(5):441-9, 2000.
Coletti D., Silvestroni L., Naro F., Molinaro M., Adamo S., Palleschi S. Vesicle-mediated phosphatidylcholine reapposition to the plasma membrane following hormone-induced phospholipase D activation. Exp Cell Res, 256(1):94-104, 2000.
Teodori L., Tagliaferri F., Stipa F., Valente M. G., Coletti D., Manganelli A., Guglielmi M., Santoro D’Angelo L., Shafer H., Gohde W. Selection, establishment and characterization of cell lines derived from a chemically-induced rat mammary heterogeneous tumor, by flow cytometry, transmission electron microscopy, and immunohistocheminstry. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal, 36(3):153-62, 2000.
Tagliaferri F., Teodori L., Valente M. G., Stipa F., Cucina A., Gohde W., Coletti D., Alo P., Stipa S. In vitro proliferation and in vivo malignancy of cell lines simultaneously derived from a chemically-induced heterogeneous rat mammary tumor. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal, 36(3):163-6, 2000.
Catizone A., Chiantore M.V., Andreola F., Coletti D., Medolago Albani L., Alescio T. Non-specific pinocytosis by human endothelial cells cultured as multicellular aggregates: uptake of lucifer yellow and horse radish peroxidase. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 42(8):1229-42, 1996.
Catizone A., Chiantore M.V., Andreola F., Coletti D., Medolago Albani L., Alescio T. Non-specific pinocytosis in in vitro reaggregated human endothelial cells: incorporation of horse radish peroxidase. In: E. Bonucci (ed.): «Report on Biology and pathology of cell-matrix interactions», 13-22, Cooperativa Libraria Editrice, Padova, 1996.
Catizone A., Chiantore M.V., Andreola F., Coletti D., Medolago Albani L., Alescio T. Non-specific pinocytosis and its dependence on cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions: incorporation of LY by human endothelial cells cultured in suspension. In: E. Bonucci (ed.): «Biology and pathology of cell-matrix interactions», 25-32, Cooperativa Libraria Editrice, Padova, 1994.
No comments:
Post a Comment